Hesperidin Market: Introduction
According to a recent study conducted on hesperidin by Transparency Market Research, the market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.3% to reach US$ 384.3 Mn by the end of the forecast period. Hesperidin is a flavanone glycoside, which is classified as a citrus bioflavonoid and majorly found in citrus fruits such as oranges, tangerines, lemon. Hesperidin is largely used in pharmaceutical applications to treat hemorrhoids, varicose veins, and improve blood circulation. It also possesses anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and anti-bacterial properties.
Get Brochure of the Report @https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=B&rep_id=44691
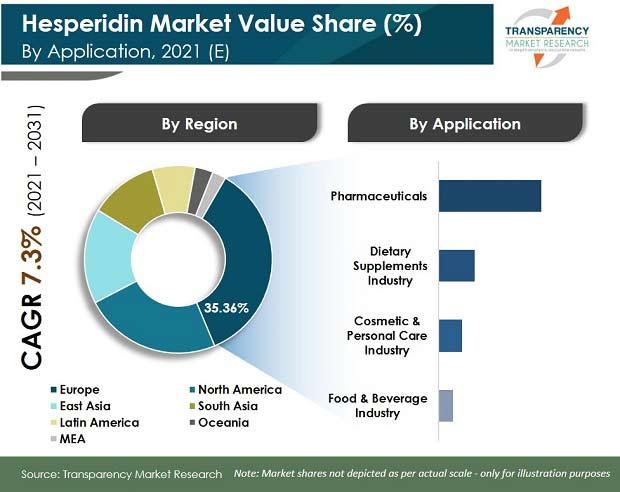
The European market for hesperidin holds majority value share of more than 35% of the global hesperidin market. It is estimated to be valued at US$ 67.2 Mn in 2021 and is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% to reach US$ 125.5 Mn by 2031 in the region.
Enquiry Before Buying:https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=EB&rep_id=44691
Benefits of Hesperidin for Cutaneous Functions to Provide Opportunity for Market Growth
Hesperidin have several benefits for cutaneous functions in recent clinical research in the field of bioflavonoids. Hesperidin’s antioxidant capabilities and promotion of epidermal proliferation, differentiation, and lipid creation aid in the improvement and enhancement of cutaneous functions. The usage of safe and effective chemicals such as hesperidin is becoming increasingly vital as the incidence of adverse cutaneous reactions to skincare products rises; this is offering promising opportunities for manufacturers to research and develop new products.
Enhancement of the epidermal permeability barrier function, reduction of UV-induced cutaneous damage, utilization as a skin whitening agent, acceleration of cutaneous wound healing, attenuation of inflammation are a few skincare functions of hesperidin in the cosmetics and healthcare industries.
As a result, growing number of bioflavonoid clinical studies and increasing use of hesperidin for a variety of cutaneous activities will present the market with prospective growth possibilities.
Intensive R&D of Hesperidin to Offer Lucrative Growth Opportunities
In the phytochemical market, research and development is essential to develop new ingredients to cater to the growing need of customers. Producers are investing much in research and development in order to broaden the scope of their products’ applications. The use of phytochemicals such as hesperidin has increased in recent years as a result of their numerous functional and therapeutic qualities.
Citrus flavonoids such as hesperidin contain therapeutic characteristics that help to treat infectious infections, reduce tooth plaque, and alleviate the symptoms of oral ailments. Further advancements in the application of hesperidin will present the product with profitable growth potential in the global market.
- To develop the best possible products for diverse sectors, Auraleafs Labs Private Limited relies on research and development. It also works on client-specific products and is always looking for ways to cut costs and standardize products.
Get Trending Report-https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2022/03/15/2403731/0/en/Animal-Feed-Amino-Acids-Market-to-Develop-at-CAGR-of-5-3-during-Forecast-Period-Notes-TMR-Study.html
Increasing Demand for Bioflavonoids in Treatment of Ocular Diseases to Drive Global Market
Bioflavonoids have risen in popularity in the recent years as a result of their growing medicinal applications. They have proven significant in improving human health and are commonly used as nutritional supplements. Hesperidin and other bioflavonoids are also used to prevent eye illnesses that cause vision loss, such as macular degeneration, cataracts, and diabetic retinopathy.
Hesperidin has excellent ocular bioavailability, making them ideal for the treatment of ocular disorders. The therapeutic application of bioflavonoids via systematic administration results in a highly effective solution in the ocular tissues at a lower dose, which aids in the fight against ocular illnesses and other infections.
Bioflavonoids have anti-angiogenic and antioxidant characteristics, as well as the ability to lower fluid retention and strengthen capillary walls. They also improve blood flow in the ophthalmic artery, which lowers the risk of glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and macular degeneration.